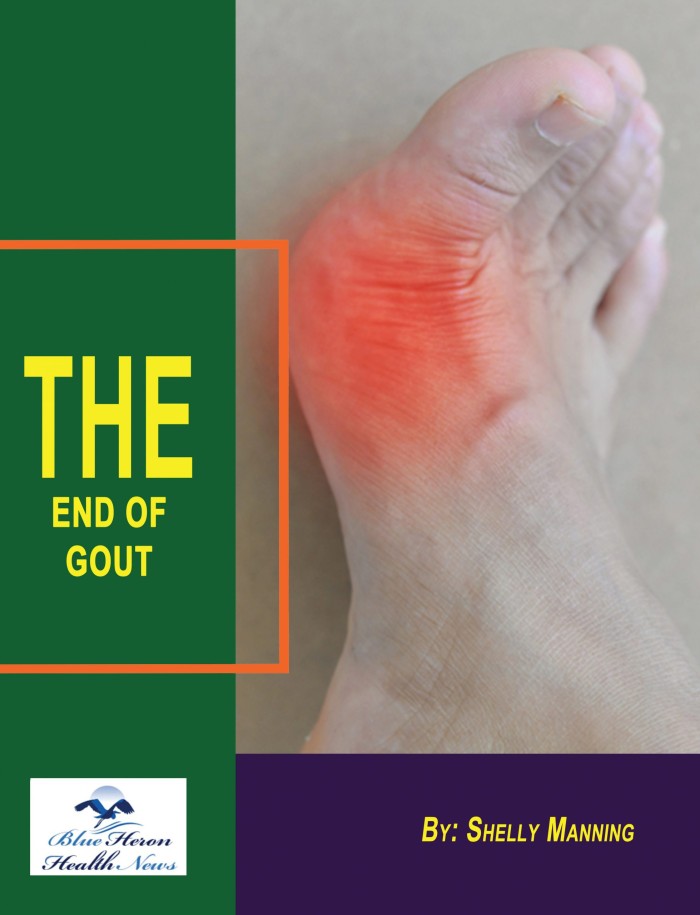
End Of GOUT Program™ By Shelly Manning The End of Gout Program is an intensive lifestyle guide and diet therapy to treat gout. It aids in minimizing and treating the uncomfortable and painful signs of gout naturally and safely. It will teach the impacted everything regarding the condition. This natural program eliminates triggers and factors that give rise to symptoms. The recommendations are honest, effective, safe, and science-based. The program treats you inside out with gout by attacking the cause. By just signing in, you get to access all the valuable information and make your life gout-free. The program has a 60-day money-back too for risk-free use. Several users have expressed their 100 percent satisfaction and results. Give it a try, and you are sure to be surprised by the fantastic results.
What is a synovial fluid analysis?
A synovial fluid analysis is a medical test used to evaluate the fluid found in the cavities of joints, known as synovial fluid. This analysis helps diagnose various joint disorders, including infections, arthritis (like gout or rheumatoid arthritis), and joint injuries. The test involves extracting a small sample of synovial fluid from the affected joint using a procedure called arthrocentesis or joint aspiration, and then examining it in a laboratory.
Purpose of Synovial Fluid Analysis
Synovial fluid analysis is primarily used to:
- Diagnose or rule out gout: Detect the presence of uric acid crystals, which confirm a diagnosis of gout.
- Identify infections (septic arthritis): Detect bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms causing joint infections.
- Differentiate between types of arthritis: Helps distinguish between various forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or psoriatic arthritis.
- Evaluate joint inflammation: Determines the severity of inflammation in the joint, which is useful for diagnosing inflammatory conditions like lupus or ankylosing spondylitis.
- Detect bleeding in the joint: Blood in the synovial fluid can indicate trauma or a bleeding disorder.
How the Procedure Works (Arthrocentesis)
- Preparation: The area around the affected joint is cleaned and sterilized, and local anesthesia is applied to minimize discomfort.
- Needle Insertion: A needle is inserted into the joint space, and synovial fluid is drawn out using a syringe. The procedure usually takes only a few minutes and is often performed in a doctor’s office or outpatient setting.
- Post-procedure: Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a lab for analysis. After the procedure, some people may experience temporary discomfort or swelling at the site, but this usually resolves quickly.
What the Analysis Involves
In the lab, the synovial fluid is evaluated for several characteristics:
- Appearance:
- Normal synovial fluid is clear, colorless, or pale yellow, and viscous.
- Cloudy or discolored fluid may indicate infection, inflammation, or the presence of crystals (as seen in gout or pseudogout).
- Microscopic Examination:
- Crystal Analysis: This is key for diagnosing gout or pseudogout. The lab checks for uric acid crystals (which indicate gout) or calcium pyrophosphate crystals (which suggest pseudogout) under a special polarized light microscope.
- White Blood Cell Count: An elevated number of white blood cells can indicate inflammation or infection.
- Bacteria Detection: If an infection is suspected, the fluid is cultured to detect bacterial growth.
- Chemical Tests:
- Glucose Levels: Lower-than-normal glucose levels in synovial fluid can point to an infection or inflammation.
- Protein Levels: Elevated protein levels may indicate inflammatory arthritis or infection.
- Gram Stain and Culture:
- If septic arthritis (joint infection) is suspected, a Gram stain is performed to identify bacteria, and a culture of the fluid may be grown to pinpoint the specific infectious organism.
Conditions Diagnosed by Synovial Fluid Analysis
Synovial fluid analysis helps in diagnosing a range of conditions, such as:
- Gout: Identified by the presence of needle-shaped uric acid crystals.
- Pseudogout: Identified by rhomboid-shaped calcium pyrophosphate crystals.
- Septic arthritis: Identified by the presence of bacteria or other signs of infection in the joint.
- Osteoarthritis: Non-inflammatory, with relatively normal synovial fluid findings.
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other inflammatory types of arthritis: Marked by high white blood cell counts and other inflammatory markers in the fluid.
Conclusion
A synovial fluid analysis is a valuable diagnostic tool for identifying the underlying cause of joint pain, inflammation, and swelling. By analyzing the fluid for crystals, bacteria, white blood cells, and other substances, doctors can determine whether the issue is related to gout, infection, or another joint condition, allowing for appropriate treatment to be initiated.
End Of GOUT Program™ By Shelly Manning The End of Gout Program is an intensive lifestyle guide and diet therapy to treat gout. It aids in minimizing and treating the uncomfortable and painful signs of gout naturally and safely. It will teach the impacted everything regarding the condition. This natural program eliminates triggers and factors that give rise to symptoms. The recommendations are honest, effective, safe, and science-based. The program treats you inside out with gout by attacking the cause. By just signing in, you get to access all the valuable information and make your life gout-free. The program has a 60-day money-back too for risk-free use. Several users have expressed their 100 percent satisfaction and results. Give it a try, and you are sure to be surprised by the fantastic results.